GORE® VIABAHN® Device family
Treatment Options
Join the next generation of care in the treatment of aortoiliac occlusive disease
Covered stents: Promising advantages for complex lesions
Covered stents help address the shortcomings of bare metal stents1-3 in treating complex aortoiliac occlusive disease (AIOD) by:
- Excluding plaque.
- Preventing in-stent neointimal hyperplasia.2-4
- Decreasing the risk of complications caused by distal embolization, perforation, rupture and dissection.5,6
- Covering and sealing off vessel ruptures.
- Promoting hemodynamic flow via a new flow lumen.
The Society for Vascular Surgery recommends covered stent grafts in instances of severe calcification at risk of vessel rupture.6
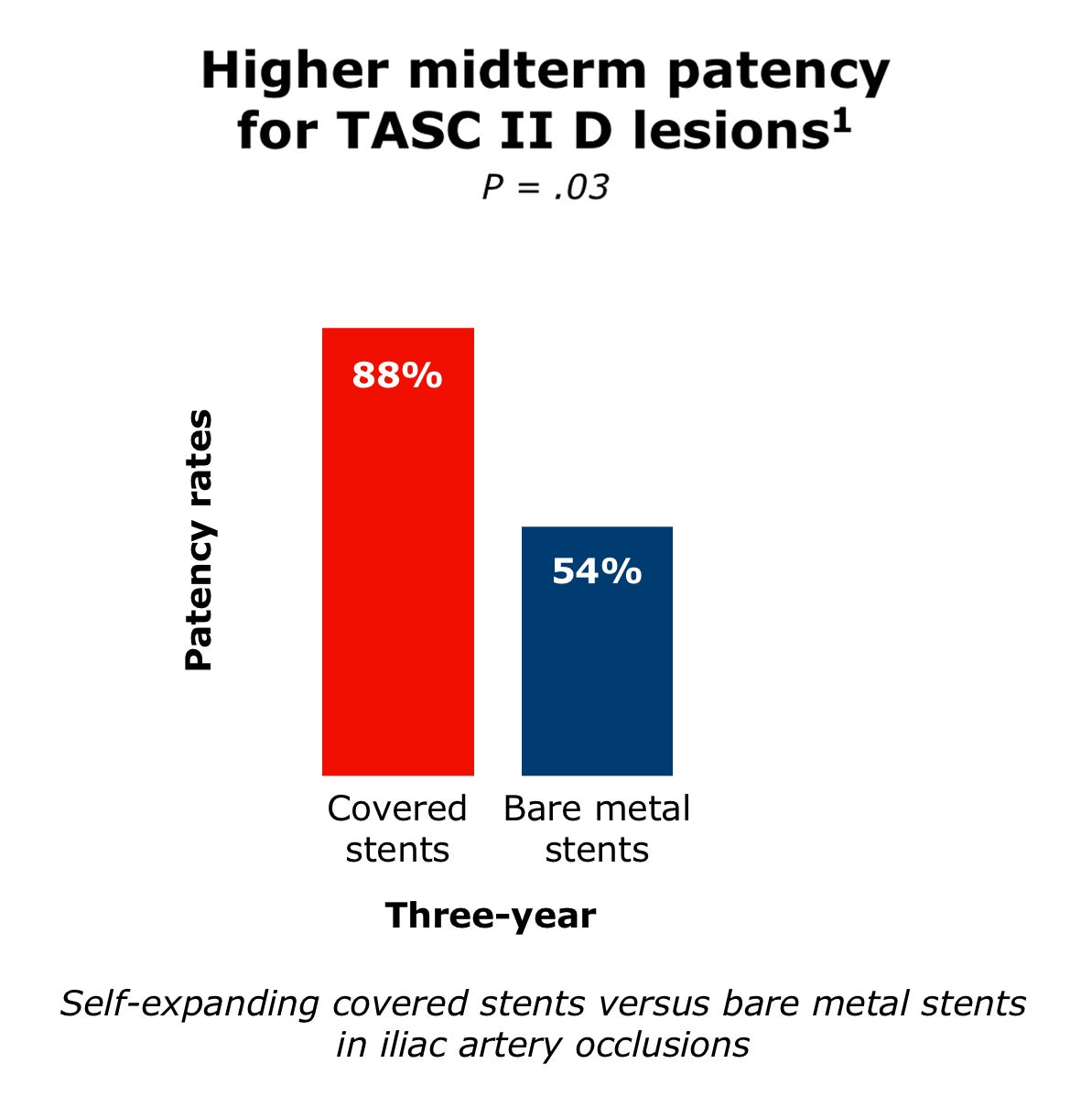
Covered stent grafts have shown excellent outcomes for treating complex AIOD
Image
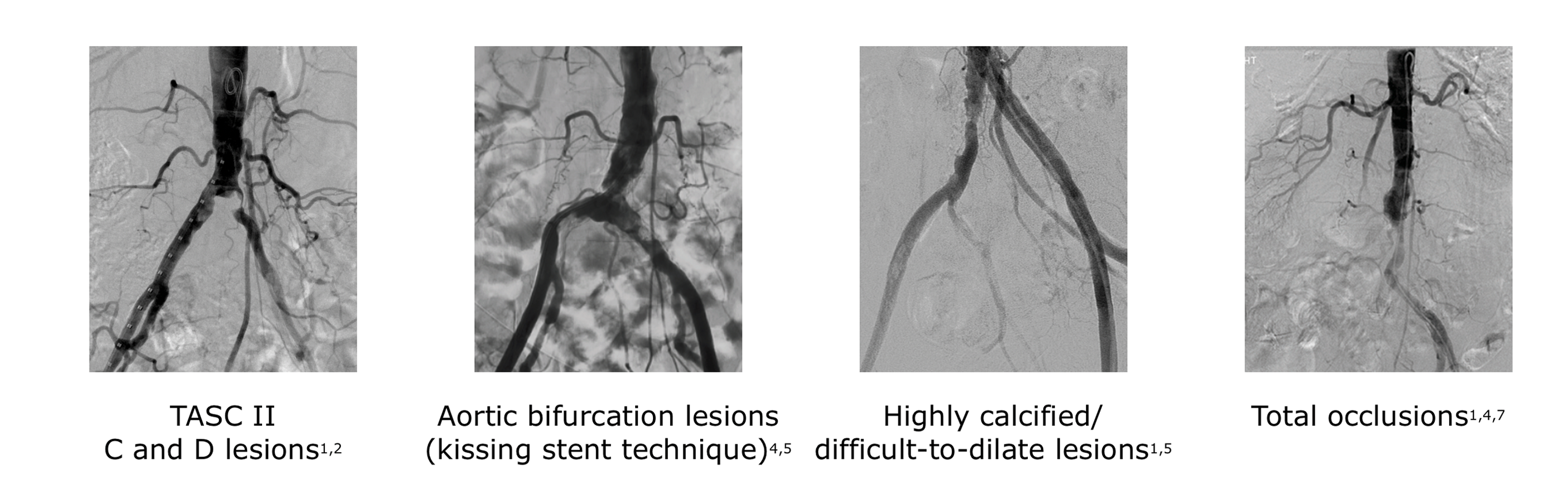
Covered stents have demonstrated:
Image
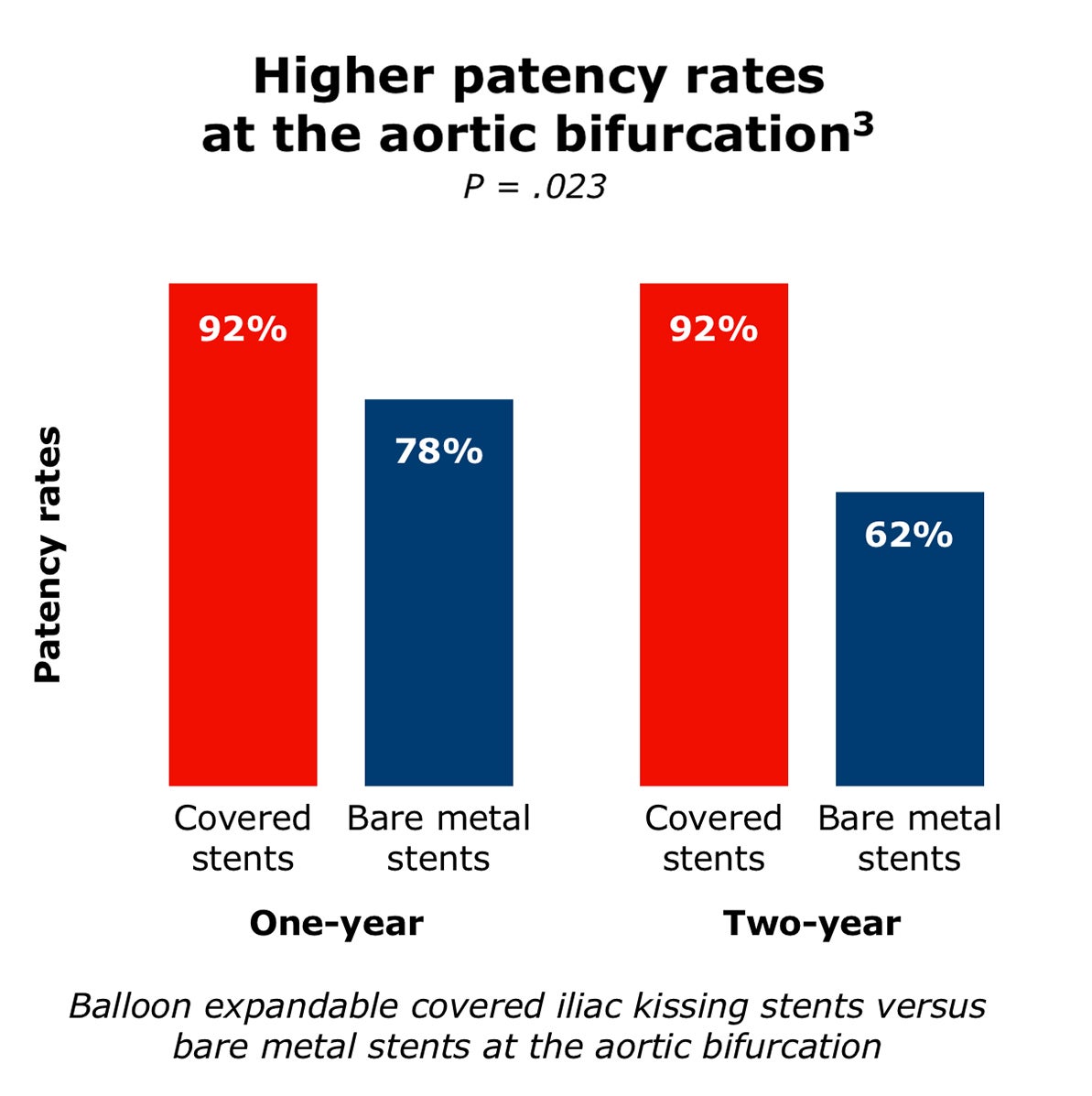
Image
Additional patient benefits versus baseline
A systematic review and meta-analysis of two randomized controlled trials and four retrospective cohort studies (N = 744) compared outcomes with covered and uncovered stents when treating AIOD.8
The covered stent group demonstrated:
+ 0.8 higher
ankle-brachial index
(Mean difference: .08, 95% CI .07 to .09, < .001)
81% lower
odds of reintervention
(Odds ratio: .19, 95% CI .09 to .042, P < .001)
* As used by Gore, Heparin Bioactive Surface refers to Gore’s proprietary CBAS Heparin Surface.
- Piazza M, Squizzato F, Dall'Antonia A, et al. Outcomes of self expanding PTFE covered stent versus bare metal stent for chronic iliac artery occlusion in matched cohorts using propensity score modelling. European Journal of Vascular & Endovascular Surgery 2017;54(2):177-185.
- Mwipatayi BP, Sharma S, Daneshmand A, et al; COBEST co-investigators. Durability of the balloon-expandable covered versus bare-metal stents in the Covered versus Balloon Expandable Stent Trial (COBEST) for the treatment of aortoiliac occlusive disease. Journal of Vascular Surgery 2016;64(1):83-94.e1.
- Sabri SS, Choudhri A, Orgera G, et al. Outcomes of covered kissing stent placement compared with bare metal stent placement in the treatment of atherosclerotic occlusive disease at the aortic bifurcation. Journal of Vascular & Interventional Radiology 2010;21(7):995-1003.
- Bismuth J, Gray BH, Holden A, Metzger C, Panneton J; VBX FLEX Study Investigators. Pivotal study of a next-generation balloon-expandable stent-graft for treatment of iliac occlusive disease. Journal of Endovascular Therapy 2017;24(5):629-637.
- Squizzato F, Piazza M, Pulli R, et al; ILIACS Registry Group. Covered versus bare metal kissing stents for reconstruction of the aortic bifurcation in the ILIACS registry. Journal of Vascular Surgery. In press.
- Society for Vascular Surgery Lower Extremity Guidelines Writing Group, Conte MS, Pomposelli FB, et al. Society for Vascular Surgery practice guidelines for atherosclerotic occlusive disease of the lower extremities: management of asymptomatic disease and claudication. Journal of Vascular Surgery 2015;61(3) Supplement:2S-41S.
- Laird JR, Zeller T, Holden A, et al; BOLSTER Investigators. Balloon-expandable vascular covered stent in the treatment of iliac artery occlusive disease: 9-month results from the BOLSTER Multicenter Study. Journal of Vascular & Interventional Radiology 2019;30(6):836-844.e1.
- Hajibandeh S, Hajibandeh S, Antoniou SA, Torella F, Antoniou GA. Covered vs uncovered stents for aortoiliac and femoropopliteal arterial disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Journal of Endovascular Therapy 2016;23(3):442-452.
