Long lesions of the superficial femoral artery (SFA) present complex challenges for endovascular management
As lesion length increases, treatment outcomes typically worsen, with decreased patency demonstrated in studies of drug-eluting stents, drug-coated balloons and bare metal stents.1-7
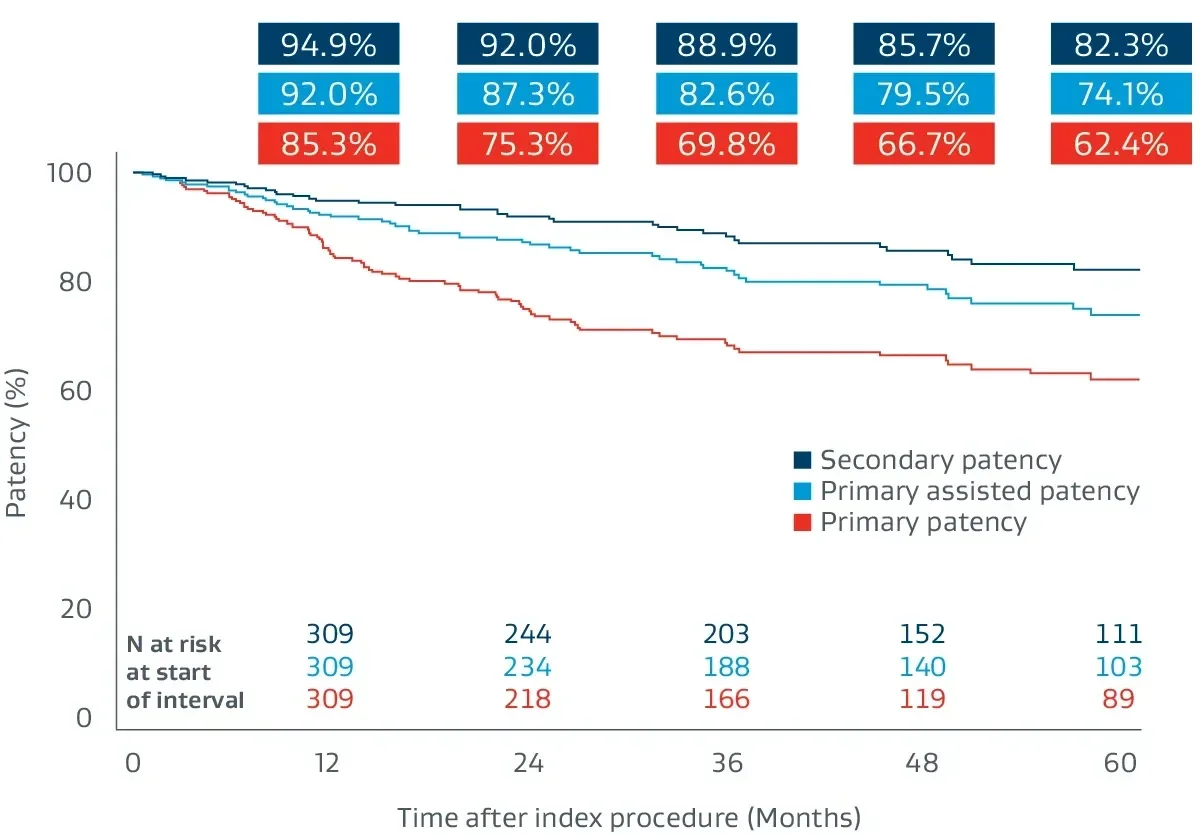
Proven outcomes in long SFA lesions
The GORE® VIABAHN® Endoprosthesis with Heparin Bioactive Surface*,† has demonstrated excellent patency and durability independent of lesion length.4, 8-11
Peer-Reviewed Results
Access the published study outcomes in Vascular Medicine, the official journal of the Society for Vascular Medicine.
Objective and methodology
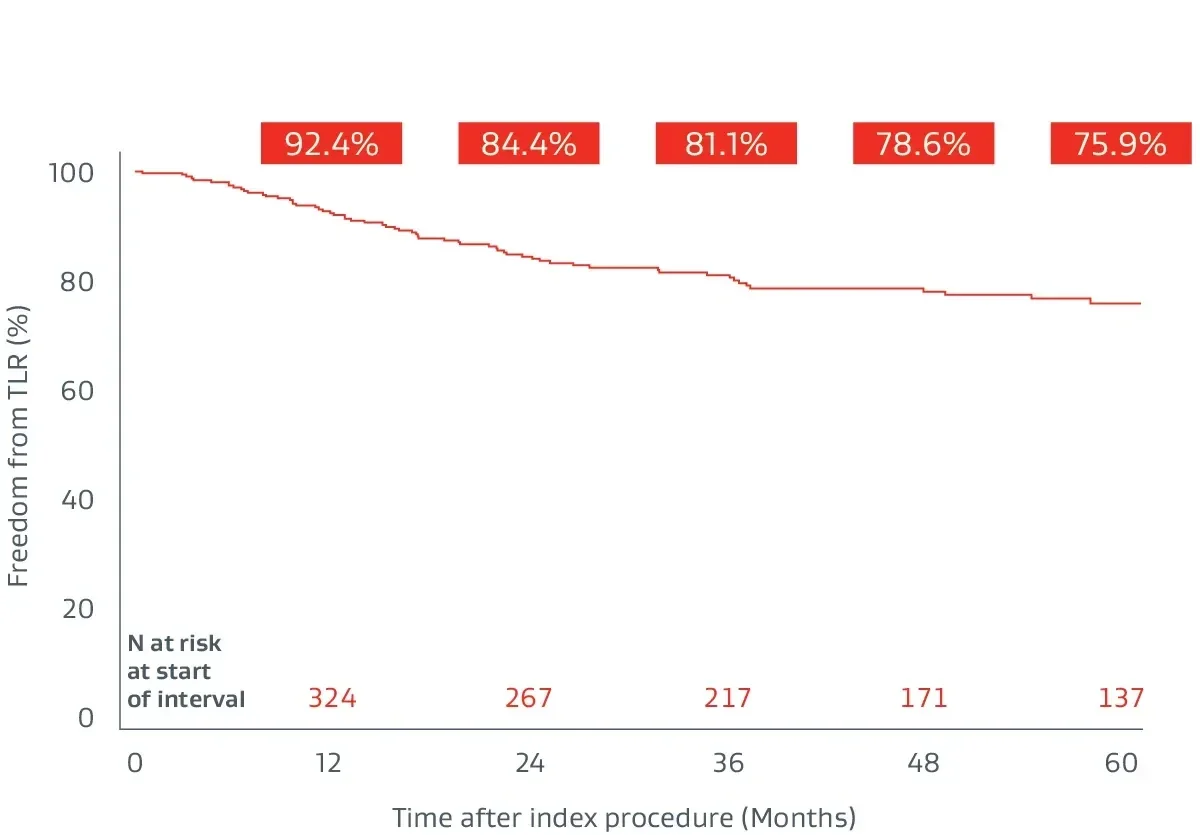
Prospective, multicenter (64 sites), 5-year follow-up builds on 1-year post-market surveillance.12, 13
- 324 lesions, 24 cm average lesion length
- 70% chronic total occlusions (CTOs)
- 27% critical limb-threatening ischemia (CLTI)
- 48% TASC II D lesions
Durable clinical outcomes
The following outcomes were first presented during the late-breaking clinical trials session at VIVA 2023.
See the results
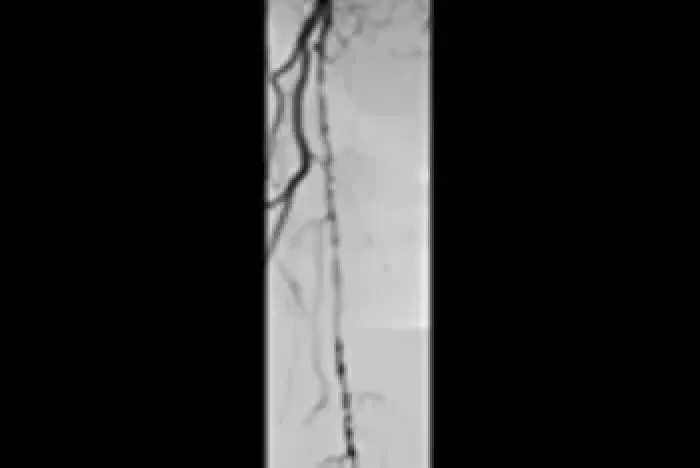
Six-year follow-up imaging shows freedom from re-occlusion despite significant popliteal lesion progression caused by chronic atherosclerotic disease.
Initial Angiograms
Prior to treatment with the VIABAHN® Device
Proximal SFA
Distal SFA
Six-year follow-up angiograms
Patency maintained with the VIABAHN® Device
Proximal SFA
Distal SFA
Images courtesy of Osamu Iida, M.D. Used with permission.
Extending a robust evidence base
Proven patency in complex SFA lesions across 7 multicenter, prospective, randomized or single-arm studies.4,8-12,14
1,089
lesions studied
71%
chronic total occlusions (CTO)
23 cm
average lesion length‡
80%
average primary patency§
Consider the demands of treating long-length lesions of the SFA
- Lesion length is a predictor of patency outcomes for several treatment modalities.
- Drug-eluting stents
- Lesion length has been shown to be an independent predictor of restenosis.1
- In a randomized study, COOK® ZILVER® PTX® Drug-Eluting Peripheral Stent has been shown to have lower patency in long lesions > 10 cm compared to those 10 cm or shorter.2
- Lesion length has been shown to be an independent predictor of restenosis.1
- Drug coated balloon (DCB)
- Multivariate analysis of the Medtronic IN.PACT Global Study demonstrated that increasing lesion length was a predictor of increased risk for Clinically Driven Target Lesion Revascularization (CD TLR).3
- Multivariate analysis of the Medtronic IN.PACT Global Study demonstrated that increasing lesion length was a predictor of increased risk for Clinically Driven Target Lesion Revascularization (CD TLR).3
- Bare metal stents (BMS)
- The VIASTAR Trial demonstrated BMS had lower patency when treating lesions > 20 cm than when treating lesions shorter than 20 cm.4
- The VIASTAR Trial demonstrated BMS had lower patency when treating lesions > 20 cm than when treating lesions shorter than 20 cm.4
- Drug-eluting stents
- Complications increase with lesion length
- Risk of dissection when using DCB increases with lesion length.5
- For many BMS, the risk of stent fracture increases with lesion length and is associated with a loss of patency.6,7
- Risk of dissection when using DCB increases with lesion length.5
* As used by Gore, Heparin Bioactive Surface refers to Gore’s proprietary CBAS® Heparin Surface
† Also referred to as the GORE® VIABAHN® Endoprosthesis with PROPATEN Bioactive Surface in some regions
‡ Weighted average lesion length.
§ One-year weighted average primary patency.
1. Iida O, Takahara M, Soga Y, et al; ZEPHYR Investigators. 1-year results of the ZEPHYR Registry (Zilver PTX for the Femoral Artery and Proximal Popliteal Artery): predictors of restenosis. JACC: Cardiovascular Interventions 2015;8(8):1105-1112.
2. Bausback Y. 2 year results of the REAL PTX Randomized Clinical Trial comparing Zilver PTX DES vs. DCB in femoropopliteal lesions. Presented at the 7th Munich Vascular Conference (MAC); December 7-9, 2017; Munich, Germany.
3. Micari A, Brodmann M, Keirse K, et al; IN.PACT Global Study Investigators. Drug-coated balloon treatment of femoropopliteal lesions for patients with intermittent claudication and ischemic rest pain: 2-year results from the IN.PACT Global Study. JACC: Cardiovascular Interventions 2018;11(10):945-953.
4. Lammer J, Zeller T, Hausegger KA, et al. Heparin-bonded covered stents versus bare-metal stents for complex femoropopliteal artery lesions: the randomized VIASTAR trial (Viabahn endoprosthesis with PROPATEN bioactive surface [VIA] versus bare nitinol stent in the treatment of long lesions in superficial femoral artery occlusive disease). Journal of the American College of Cardiology 2013;62(15):1320-1327.
5. Brodmann M. Real world value of the In.Pact Admiral DCB (Medtronic) for fem-pop lesions: from the In.Pact Global Registry: what else does it tell us. Presented at the 44th Annual Symposium on Vascular and Endovascular Issues, Techniques, Horizons (VEITHsymposium); November 14-18, 2017; New York, NY.
6. Iida O, Nanto S, Uematsu M, Ikeoka K, Okamoto S, Nagata S. Influence of stent fracture on the long-term patency in the femoro-popliteal artery. JACC : Cardiovascular Interventions 2009;2(7):665-671.
7. Scheinert D, Scheinert S, Sax J, et al. Prevalence and clinical impact of stent fractures after femoropopliteal stenting. Journal of the American College of Cardiology 2005;45(2):312-315.
8. Zeller T, Peeters P, Bosiers M, et al. Heparin-bonded stent-graft for the treatment of TASC II C and D femoropopliteal lesions: the Viabahn-25 cm Trial. Journal of Endovascular Therapy 2014;21(6):765-774.
9. Reijnen MMPJ, van Walraven LA, Fritschy WM, et al. 1-year results of a multicenter, randomized controlled trial comparing heparin-bonded endoluminal to femoropopliteal bypass. Journal of Cardiovascular Interventions 2017;10(22):2320-2331.
10. Ohki T, Kichikawa K, Yokoi H, et al. Long-term results of the Japanese multicenter Viabahn trial of heparin bonded endovascular stent grafts for long and complex lesions in the superficial femoral artery. Journal of Vascular Surgery 2021;74(6):1958-1967.e2. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0741521421010119
11. Saxon RR, Chervu A, Jones PA, et al. Heparin‑bonded, expanded polytetrafluoroethylene‑lined stent graft in the treatment of femoropopliteal artery disease: 1‑year results of the VIPER (Viabahn Endoprosthesis with Heparin Bioactive Surface in the Treatment of Superficial Femoral Artery Obstructive Disease) Trial. Journal of Vascular & Interventional Radiology 2013;24(2):165‑173.
12. Iida O, Ohki T, Soga Y, et al. Twelve-month outcomes from the Japanese post-market surveillance study of the Viabahn Endoprosthesis as treatment for symptomatic peripheral arterial disease in the superficial femoral arteries. Journal of Endovascular Therapy 2022;29(6):855-865.
13. Iida O, Ohki T, Soga Y, et al. Five-Year outcomes of the GORE VIABAHN Endoprosthesis for the treatment of complex femoropopliteal lesions from a Japanese post-market surveillance study. Vascular Medicine 2024;29(4):416-423.
14. Iida O, Takahara M, Soga Y, et al; VANQUISH Investigators. One-year outcomes of heparin-bonded stent-graft therapy for real-world femoropopliteal lesions and the association of patency with the prothrombotic state based on the prospective, observational, multicenter Viabahn Stent-Graft Placement for Femoropopliteal Diseases Requiring Endovascular Therapy (VANQUISH) Study. Journal of Endovascular Therapy 2021;28(1):123-131.
15. GORE® VIABAHN® Endoprosthesis with Heparin Bioactive Surface Instructions for Use (IFU). W. L. Gore & Associates, Inc. Accessed August 9, 2023. https://eifu.goremedical.com
COOK and ZILVER PTX are trademarks of Cook Medical, Inc.

Refer to Instructions for Use at eifu.goremedical.com for a complete description of all applicable indications, warnings, precautions and contraindications for the markets where this product is available. RXOnly
INDICATIONS FOR USE IN THE U.S.: The GORE® VIABAHN® Endoprosthesis with Heparin Bioactive Surface is indicated for improving blood flow in patients with symptomatic peripheral arterial disease in superficial femoral artery de novo and restenotic lesions up to 270 mm in length with reference vessel diameters ranging from 4.0 – 7.5 mm. The GORE® VIABAHN® Endoprosthesis with Heparin Bioactive Surface is indicated for improving blood flow in patients with symptomatic peripheral arterial disease in superficial femoral artery in-stent restenotic lesions up to 270 mm in length with reference vessel diameters ranging from 4.0 – 6.5 mm. The GORE® VIABAHN® Endoprosthesis with Heparin Bioactive Surface is indicated for improving blood flow in patients with symptomatic peripheral arterial disease in iliac artery lesions up to 80 mm in length with reference vessel diameters ranging from 4.0 – 12 mm. The GORE® VIABAHN® Endoprosthesis with Heparin Bioactive Surface is also indicated for the treatment of stenosis or thrombotic occlusion at the venous anastomosis of synthetic arteriovenous (AV) access grafts.
CONTRAINDICATIONS: The GORE® VIABAHN® Endoprosthesis with Heparin Bioactive Surface is contraindicated for non-compliant lesions where full expansion of an angioplasty balloon catheter was not achieved during pre-dilatation, or where lesions cannot be dilated sufficiently to allow passage of the delivery system. Do not use the GORE® VIABAHN® Endoprosthesis with Heparin Bioactive Surface in patients with known hypersensitivity to heparin, including those patients who have had a previous incident of Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia (HIT) type II.