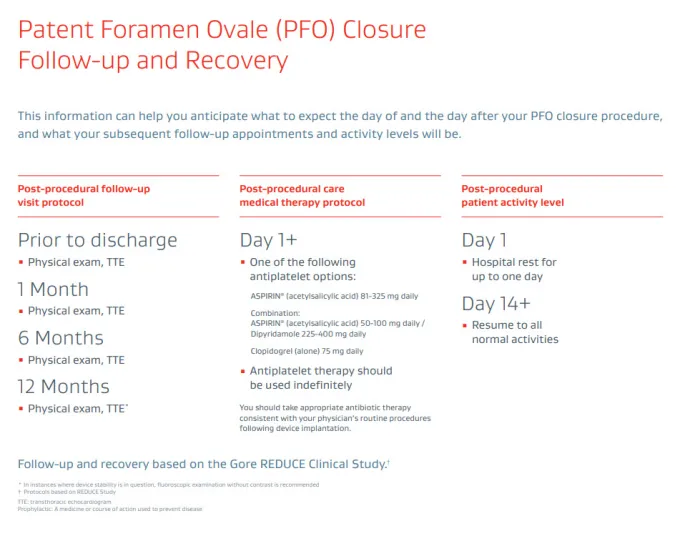
GORE® CARDIOFORM Septal Occluder for PFO Closure
Redefining STROKE PREVENTION
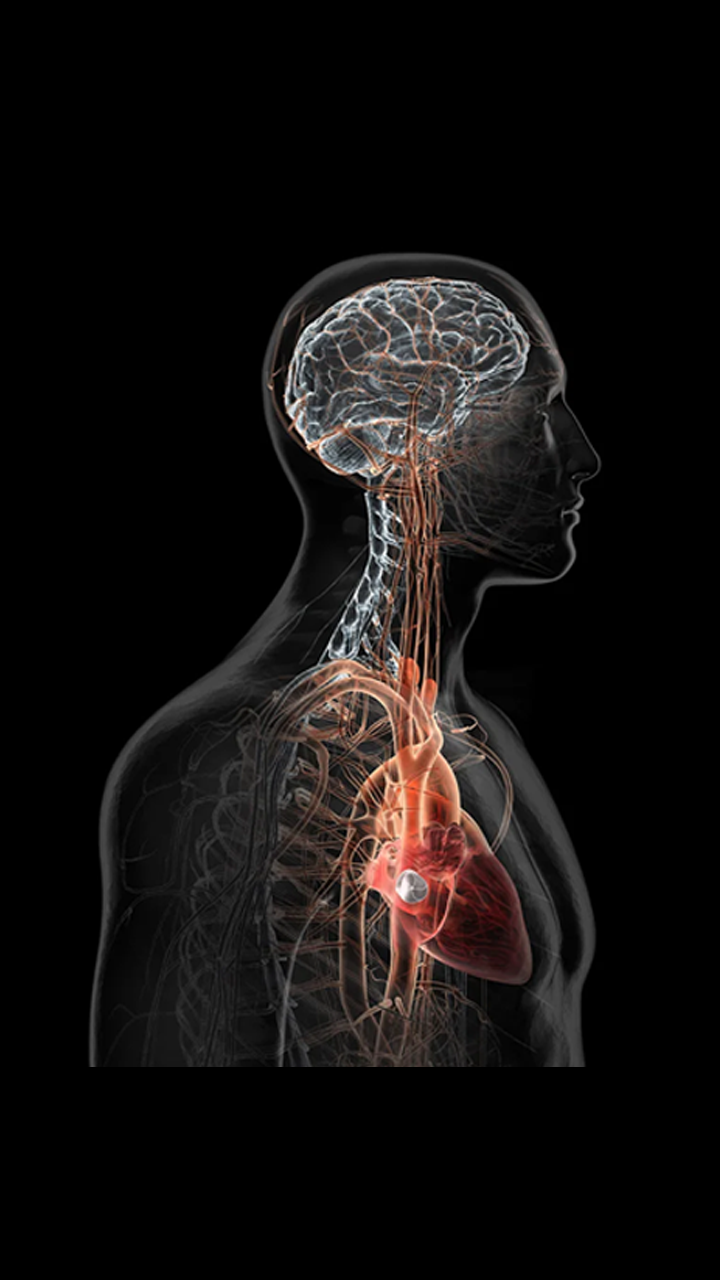
The “Hole” Truth about Cryptogenic Stroke
Learn more about patent foramen ovale (PFO) and talk with your healthcare professional to see if closing the hole in your heart can help reduce the risk of another stroke.
Educational Videos
PFO and stroke animation
Watch how a PFO may permit a blood clot to pass from the right side of the heart to the left side possibly leading to a stroke.
Could a PFO have contributed to your cryptogenic stroke?
Learn the basics about cryptogenic stroke, PFO and the PFO closure procedure.
PFO closure animation
Watch how the GORE® CARDIOFORM Septal Occluder closes a PFO.
Kathryn's journey
Are you young and healthy, but have had a stroke? You are not alone. See what Kathryn decided to do to reduce her chance of another stroke.
Educational Material
Quick Facts about Stroke and PFO
Stroke is the leading
preventable cause of long-term severe disability1
Stroke is the 5th leading cause of death1
1/3 of ischemic strokes
are classified as cryptogenic, or due to unknown cause2
A patent foramen ovale (PFO)
is a hole occurring in the tissue between the left and right atria of the heart
25% of people have a PFO3
Up to 40 – 50% of patients
who have had a cryptogenic stroke have a PFO3
Frequently Asked Questions
Before birth, a baby’s heart will have a hole with a flap-like covering between the upper two chambers of the heart. This opening (the foramen ovale) allows blood rich in oxygen from the mother to bypass the baby’s lungs which do not function until the baby is born. After birth, the flap-like covering will typically close the hole permanently. However, in about one out of every four individuals, the hole in the heart will remain open. This is called a patent foramen ovale or PFO.
From time to time, a PFO may permit blood to pass from the right side of the heart to the left side of the heart bypassing the normal route of going through the lungs first. In most people, a PFO creates no symptoms and requires no treatment. However, in a small minority, a PFO may permit blood clots to pass from the right side of the heart to the left side possibly leading to a stroke.
A medical team, including a neurologist and a cardiologist, will conduct tests to look for the cause of your stroke. These tests include collecting images of your brain, heart, and blood vessels (using ultrasound, CT and / or magnetic resonance imaging [MRI] scans), monitoring your heart rhythm, and blood tests. If your doctors do not find any likely cause of your stroke from this testing, they may conclude that you had a cryptogenic stroke.
A PFO is found by a cardiologist using ultrasound pictures of the heart (echocardiogram or echo). The ultrasound uses sound waves to evaluate the structure of the heart and the direction of blood flow to see if blood can pass from the right side of the heart to the left side.
If no other identifiable cause of the stroke can be found, your doctors may conclude that the PFO played an important role by permitting a blood clot to pass from the right side of your heart to the left side and blocking a blood vessel that supplies the brain.
The GORE® CARDIOFORM Septal Occluder is a minimally invasive device intended for the closure of a PFO using cardiac catheterization. It is a permanent implant consisting of a near circular wire frame covered with thin ePTFE material. The soft, conformable ePTFE material, invented and manufactured by Gore, has been used in open-heart surgery for more than 40 years and has been shown to be safe in implanted medical devices. The wire frame is made of a nickel-titanium metal alloy called nitinol with a platinum core (so that it may be seen on X-ray images).
The Gore REDUCE Clinical study demonstrated a 77% relative stroke reduction with PFO closure plus medical therapy vs. medical therapy alone*,4
The Gore REDUCE Clinical Study is the only U.S. IDE trial that achieved its primary end point and showed the largest reduction in recurrent ischemic stroke*,4 in all PFO shunt sizes over medical therapy alone.
Ask your doctor if Gore GORE® CARDIOFORM Septal Occluder is right for you.
* The REDUCE study determined safety and efficacy of patent foramen ovale (PFO) closure with the GORE® CARDIOFORM Septal Occluder or GORE® HELEX® Septal Occluder plus antiplatelet medical management compared to antiplatelet medical management alone in patients with a PFO and history of cryptogenic stroke. All PFO anatomies were incorporated into this study within indicated sizing parameters of the Instructions for Use.
- American Stroke Association. Web site. http://www.strokeassociation.org/STROKEORG/AboutStroke/Impact-of-Stroke-Stroke-statistics_UCM_310728_Article.jsp#.Wp7dIGr4-pr. Accessed March 6, 2018.
- American Heart Association / American Stroke Association, Inc. Web site. Understanding diagnosis and treatment of cryptogenic stroke. https://www.strokeassociation.org/idc/groups/stroke-public/@wcm/@hcm/@sta/documents/downloadable/ucm_477051.pdf. Published 2015. Accessed March 6, 2018.
- American Heart Association, Inc. Web site. Patent Foramen Ovale (PFO). http://www.heart.org/HEARTORG/Conditions/More/CardiovascularConditionsofChildhood/Patent-Foramen-Ovale-PFO_UCM_469590_Article.jsp#.Wp7sFWr4-pp. Published March 2017. Accessed March 6, 2018.
- Søndergaard L, Kasner SE, Rhodes JF, et al; Gore REDUCE Study Investigators. Patent foramen ovale closure or antiplatelet therapy for cryptogenic stroke. New England Journal of Medicine 2017;377(11):1033-1042.
In some jurisdictions, ASPIRIN is a trademark of Bayer Intellectual Property GmbH or its affiliated companies.
This information is intended for education and awareness only. Patients should consult their physician for information on the risks associated with the devices and surgical procedures discussed in this website. All surgical procedures carry potential health risks. Not all patients will be candidates for treatment with these devices, and individual outcomes may vary.
Always follow physician advice on your post-surgery care and recovery.
Caution: U.S. law restricts use of this device on the order of a physician (Rx).

Refer to Instructions for Use at eifu.goremedical.com for a complete description of all applicable indications, warnings, precautions and contraindications for the markets where this product is available. RXOnly
INDICATIONS FOR USE: The GORE® CARDIOFORM Septal Occluder is a permanently implanted device indicated for the percutaneous, transcatheter closure of the following defects of the atrial septum: ostium secundum atrial septal defects (ASDs); patent foramen ovale (PFO) to reduce the risk of recurrent ischemic stroke in patients, predominantly between the ages of 18 and 60 years, who have had a cryptogenic stroke due to a presumed paradoxical embolism, as determined by a neurologist and cardiologist following an evaluation to exclude known causes of ischemic stroke.
CONTRAINDICATIONS: The GORE® CARDIOFORM Septal Occluder is contraindicated for use in patients: Unable to take antiplatelet or anticoagulant medications such as aspirin, heparin or warfarin; with anatomy where the GORE® CARDIOFORM Septal Occluder size or position would interfere with other intracardiac or intravascular structures, such as cardiac valves or pulmonary veins; with active endocarditis, or other infections producing bacteremia, or patients with known sepsis within one month of planned implantation, or any other infection that cannot be treated successfully prior to device placement; with known intracardiac thrombi.